Estimating the cost of building a SaaS platform requires a detailed analysis of technical requirements, architectural complexity, and market standards. In 2026, development costs are no longer strictly a function of manual labor but are increasingly influenced by the integration of automated workflows and specialized cloud infrastructure.
The financial commitment for a SaaS project varies significantly based on its intended scale. A basic validation product is a manageable investment for many startups, while a global enterprise platform demands substantial resources for security and high-availability systems. Understanding the specific components that drive these figures is essential for effective financial planning.

SaaS Development Average Cost
In 2026, the cost of developing a SaaS application varies widely depending on complexity, feature scope, technology stack, team location (e.g., blended global rates with outsourcing), integrations, security/compliance needs, and emerging demands like AI or real-time processing.
According to recent industry reports and breakdowns (from sources like Saigon Technology, Deorwine Infotech, Innovecs, and others), here are realistic average price ranges in USD for global/mixed teams:
- Micro/MVP level (minimal viable product: core features, basic authentication, simple dashboard, limited integrations): $25,000 – $60,000 (most common starting point for idea validation; simpler versions can go as low as $20,000-$50,000, while more polished MVPs reach $60,000+).
- Basic/Simple SaaS (essential features, standard multi-tenancy, payment processing, basic UI/UX): $20,000 – $80,000-$100,000.
- Medium-level SaaS (advanced: custom roles, third-party integrations, analytics, scalable backend, moderate custom logic): $60,000 – $150,000-$300,000.
- Complex/Enterprise-level SaaS (high-load platforms, real-time data, AI modules, advanced security like GDPR/SOC 2, extensive integrations): $150,000 – $500,000+ (often up to $1,000,000+ for fully featured, scalable systems).
What Is The Price Actually Based On?
The technical scope of a SaaS application is the primary determinant of its price. Features like multi-tenancy, where a single instance of the software serves multiple customers, require a more sophisticated database architecture compared to single-user tools. In 2026, the demand for embedded analytics and real-time data processing has further specialized the development process.
Technology choices also play a critical role. Utilizing modern frameworks like React or Node.js can offer efficiency in the long term, though some specialized languages may require higher developer rates. Cloud infrastructure costs, once a minor consideration, now involve complex service-level agreements and consumption-based pricing models that must be factored into the initial build.
Cost by Feature Complexity & Level
Feature sets are categorized by their technical depth and the logic required to implement them. Basic features such as user registration and simple dashboards represent the entry point of the development scale. These components are standard across most platforms and benefit from established development patterns.
Advanced functionalities significantly shift the budget. Real-time data processing, artificial intelligence modules, and complex data reporting tools require specialized expertise. Implementing these features often involves longer development cycles and higher testing requirements to ensure system stability under load.
- Basic Level SaaS: $50,000 to $100,000
- Medium Level SaaS: $100,000 to $300,000
- Complex Level SaaS: $300,000 to $1,000,000+
- Micro/MVP Level: $5,000 to $40,000
UI/UX Design Cost for SaaS
User experience has become a primary factor in customer retention for SaaS products. In 2026, simple functional interfaces are rarely sufficient for competitive markets. Professional UI/UX design involves detailed user journey mapping, wireframing, and interactive prototyping to ensure the final product is intuitive.
High-end design often includes custom graphics, responsive layouts for multiple device types, and accessibility compliance. These elements require dedicated design teams and multiple rounds of user testing to refine the interaction models.
- Simple SaaS Design: $5,000 to $15,000
- Medium-Level Design: $15,000 to $40,000
- Complex SaaS Design: $40,000 to $100,000+
Investing in design early helps reduce development rework by identifying usability issues before the coding phase begins. A well-documented design system also allows developers to build consistent interfaces more quickly.
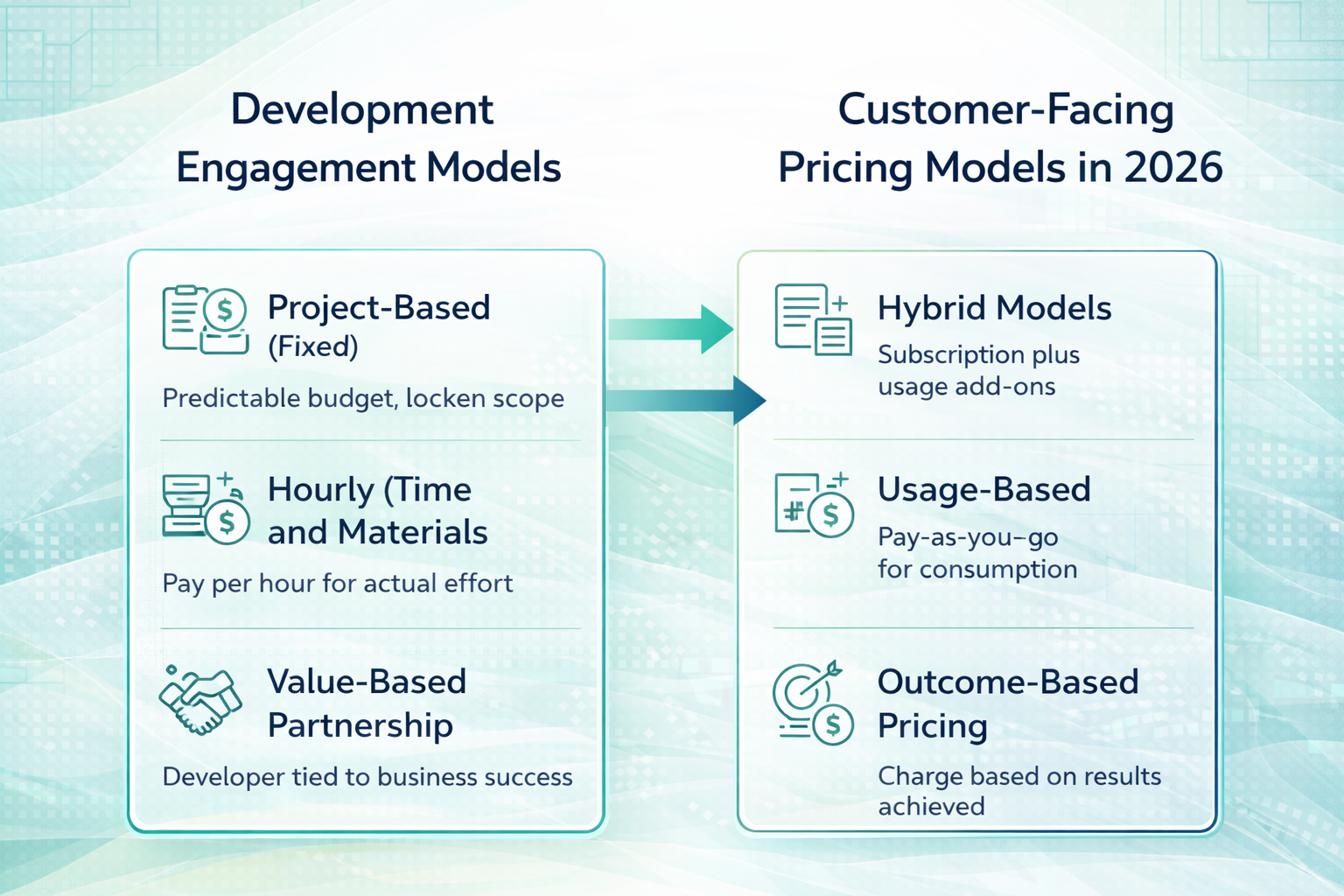
SaaS Product Development Pricing Models
In the financial landscape of 2026, the relationship between development cost and market pricing is more integrated than ever. Choosing a development payment structure and a customer monetization strategy are two sides of the same strategic coin. A mismatch between the development engagement model and the customer pricing model is one of the most common factors leading to eroded margins.
Development Engagement Models
The structure of a partnership with a development team directly affects the risk profile and initial capital requirements of a project. In the current market, three dominant models exist for funding the build phase.
Project-Based (Fixed)
This model is ideal for well-defined MVPs with a strictly locked scope. It provides high budget certainty, with costs typically ranging from $10,000 to $100,000 for standard projects. However, it lacks the flexibility to pivot based on early user feedback without incurring additional “change request” fees.
Hourly (Time and Materials)
This model is the standard for agile development in 2026. You pay for the actual effort exerted, which usually falls between $25 and $150 per hour depending on the region. It allows us to evolve the product dynamically, although it requires disciplined management to avoid “scope creep.”
Value-Based Partnership
This is a more sophisticated approach where the developer’s compensation is tied to the business value created. This might include a lower base fee combined with equity or a percentage of future revenue. It aligns the developer’s interests entirely with your success but requires a high level of mutual trust.
Customer-Facing Pricing Models in 2026
Once the product is built, how you monetize it must reflect the value it delivers. By 2026, the market has moved beyond simple “per-user” seats, especially as AI agents now perform the work that previously required multiple humans.
Hybrid Models
This is currently the most popular choice, used by nearly 60% of SaaS providers. It combines a predictable base subscription fee with usage-based add-ons. For example, a customer might pay $50/month for the platform plus a small fee per AI-generated report.
Usage-Based (Pay-As-You-Go)
This model ties costs directly to consumption, such as the number of API calls or gigabytes of data processed. It lowers the barrier to entry for small users but can make revenue forecasting more difficult for the provider.
Outcome-Based Pricing
This represents the cutting edge of SaaS monetization. Instead of charging for the tool, you charge for the result. If your SaaS helps a client save $10,000 in operational costs, you might charge a percentage of those verified savings.
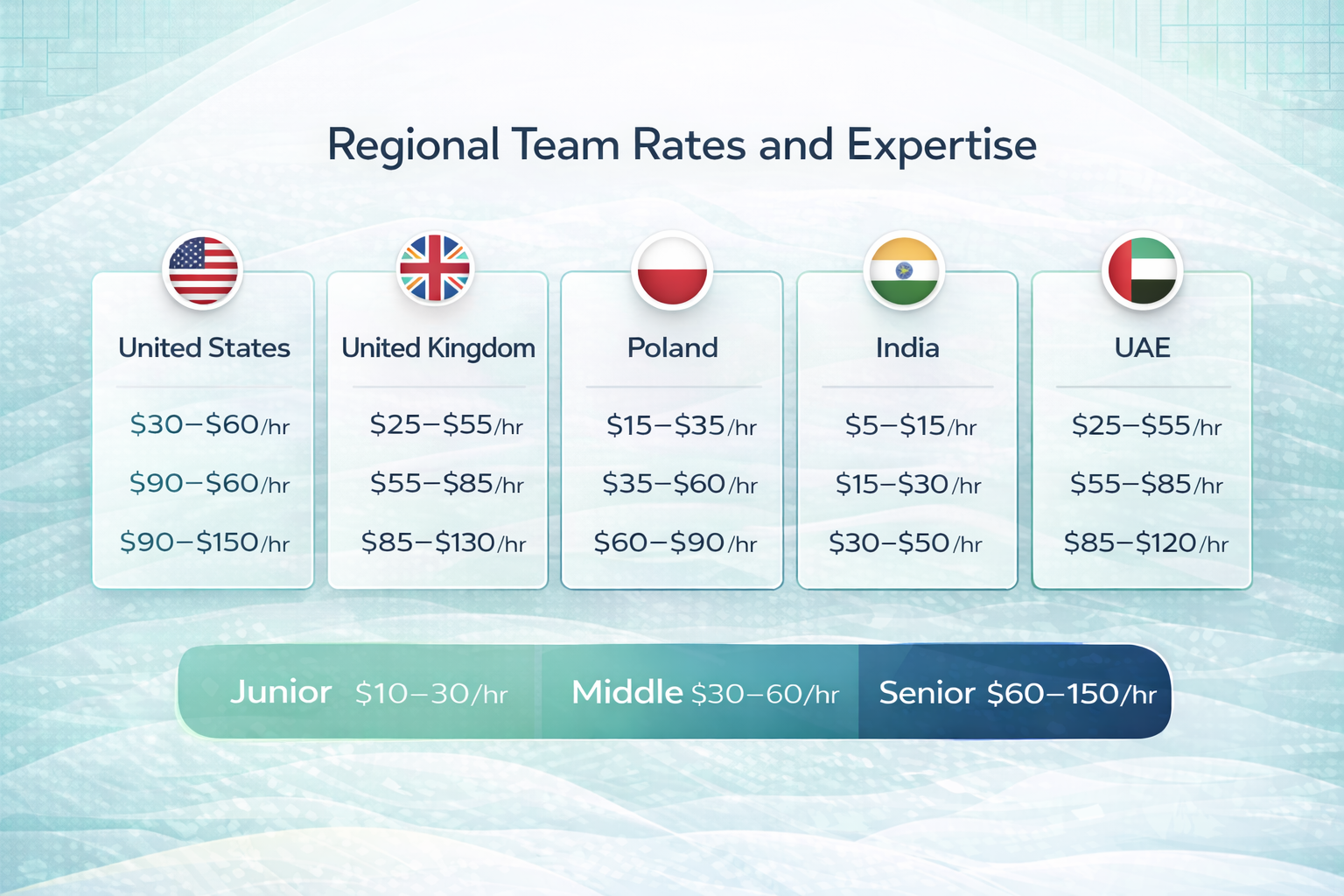
Regional Team Rates and Expertise
The geographic location of a development team remains one of the most significant variables in SaaS pricing. While the global nature of software development allows for remote collaboration, regional economic factors create wide disparities in hourly rates. Selecting a team is often a balance between budget constraints and the need for localized communication.
In 2026, high-demand markets like the United States and Northern Europe maintain the highest labor costs due to specialized talent competition. Conversely, established tech hubs in South Asia and parts of Eastern Europe provide access to similar technical skills at a lower cost per hour.
| Region | Junior Developer ($/hr) | Middle Developer ($/hr) | Senior Developer ($/hr) |
| Vereinigte Staaten | $30 – $60 | $60 – $90 | $90 – $150 |
| Vereinigtes Königreich | $25 – $55 | $55 – $85 | $85 – $130 |
| Polen | $15 – $35 | $35 – $60 | $60 – $90 |
| Indien | $5 – $15 | $15 – $30 | $30 – $50 |
| UAE | $25 – $55 | $55 – $85 | $85 – $120 |
Beyond hourly rates, the team’s internal structure affects efficiency. A team with senior architects and dedicated project managers may have a higher hourly cost but can often complete complex tasks faster than a larger group of junior developers.
Strategic Partnership as a Key Cost Factor in SaaS Application Development
When evaluating the SaaS application development cost, budget optimization in 2026 depends heavily on the chosen cooperation model. At A-Listware, we serve as a strategic execution engine that transforms ambitious SaaS visions into high-performing, market-ready platforms. We act as a trusted extension of your team, providing the technical expertise and execution power needed to bridge skill gaps and accelerate growth without the administrative friction of traditional hiring.
By focusing on seamless integration and long-term value, we ensure that every technical decision: from initial architecture to AI implementation: aligns perfectly with your broader business objectives. Our partnership model is designed for flexibility and future-ready scalability, taking full ownership of technical excellence and implementing modular architectures that prevent expensive rework. Furthermore, by implementing rigorous security standards like SOC 2 and GDPR early in the process, we ensure the product is ready for 2026 infrastructure demands while keeping the development budget significantly optimized. Empowering leadership to focus on strategy while we handle the technical heavy lifting helps achieve a faster market entry within a controlled and predictable financial framework.
Third-Party Integrations and Security
Modern SaaS applications rarely operate as isolated systems. They rely on external APIs for essential functions like payment processing, email delivery, and customer relationship management. Each integration adds a layer of complexity to the development and maintenance phases.
Security and regulatory compliance are non-negotiable for enterprise SaaS. Implementing features like multi-factor authentication, data encryption, and audit logs is necessary to meet standards such as GDPR or HIPAA. This specialized work increases the initial development time and requires ongoing security audits.
- Basic Authentication and Security: Standard in most builds.
- Einhaltung von Vorschriften: Requires specialized legal and technical review.
- Enterprise Integrations: Involves custom API development and data mapping.
- Payment Gateway Integration: Essential for subscription-based revenue models.
Third-party services also introduce ongoing costs. Subscription fees for essential APIs must be accounted for in the operational budget, as these costs scale with the number of users on the platform.

Maintenance and Quality Assurance
The launch of a SaaS application is only the beginning of its lifecycle. Quality Assurance (QA) is an ongoing process that ensures the platform remains functional as new features are added. In 2026, automated testing has become standard for maintaining the stability of complex platforms, allowing for rapid regression checks without manual overhead.
Manual testing is still used for assessing user experience and finding edge-case bugs, but it is time-intensive. A robust QA strategy typically consumes about 15% to 25% of the total development budget. Skipping this phase often leads to much higher costs in the form of emergency bug fixes and customer churn after the product reaches the market.
Maintenance involves more than just fixing errors. It is a proactive approach to keeping the system healthy and aligned with the latest technology standards. To ensure long-term stability, Focus on these key maintenance areas:
- Security Patching: Regular updates to frameworks and libraries to protect against new vulnerabilities.
- Server Monitoring: Continuous tracking of infrastructure performance to prevent downtime and optimize costs.
- API Versioning: Ensuring that third-party integrations continue to work as external services update their protocols.
- Optimierung der Leistung: Ongoing database tuning and code refactoring to maintain speed as the user base grows.
Most SaaS companies allocate 20% of their initial development cost annually to keep the platform operational and secure. This ensures the software remains compatible with evolving browser standards and operating system updates. By treating maintenance as a strategic investment, businesses can significantly reduce technical debt and maintain a high level of user trust.
Schlussfolgerung
Developing a SaaS application in 2026 is a multi-faceted investment that goes far beyond simple coding. The total cost is shaped by the complexity of the feature set, the sophistication of the user interface, and the regional rates of the development team. Starting with a clear MVP allows for market validation while keeping initial expenditures manageable.
As the platform grows, the costs shift toward scaling infrastructure and maintaining high security standards. By understanding the core drivers of SaaS expenses-from regional labor rates to the necessity of ongoing maintenance-businesses can build sustainable digital products that offer long-term value.
FAQ
- What is the average cost to build a SaaS MVP in 2026?
A basic Minimum Viable Product generally costs between $5,000 and $40,000. This version focuses on core functionality to validate the business idea with early users before committing to a full-scale build.
- How do regional developer rates affect the total budget?
Developer rates vary significantly by location, with US-based senior developers charging up to $150 per hour while senior developers in India may charge $30 to $50. This can result in a 3x to 5x difference in the total project cost.
- Why is UI/UX design so expensive in SaaS development?
Design involves extensive research, user mapping, and prototyping to ensure the application is easy to use. For complex platforms, design costs can exceed $40,000 because every interaction must be custom-built for high retention.
- What are the recurring costs after a SaaS application launch?
Post-launch costs include cloud hosting, security monitoring, and regular maintenance. Typically, these expenses amount to 20% of the initial development cost every year to ensure the software stays functional.
- How much should I budget for SaaS quality assurance?
Quality Assurance typically requires 15% to 25% of the total development budget. This covers both manual testing for usability and automated testing for long-term system stability.
- What impacts the cost of third-party integrations?
Each external service, such as Stripe for payments or HubSpot for CRM, requires custom API work. Depending on the complexity of the data sync, each integration can add several thousand dollars to the development phase.
- Is it cheaper to hire an in-house team or an agency?
Agencies are often more cost-effective for the initial build because they provide a complete team with diverse skills. In-house teams offer more control but involve significant overhead costs like salaries, benefits, and office equipment.


