Post-launch application management directly impacts operational stability. While development is often the primary focus, long-term software value depends on structured support and maintenance. In 2026, the landscape of application support has become more complex due to rapid shifts in operating system requirements, security standards, and user expectations.
Application support is not just a reactive fix for occasional glitches. It is a strategic effort to ensure that software remains functional, secure, and aligned with evolving business goals. The financial commitment required for these activities is typically a percentage of the initial investment, but the actual numbers fluctuate based on several technical and operational variables. Understanding the breakdown of these costs allows organizations to move from unplanned emergency spending to a predictable, value-driven budget.
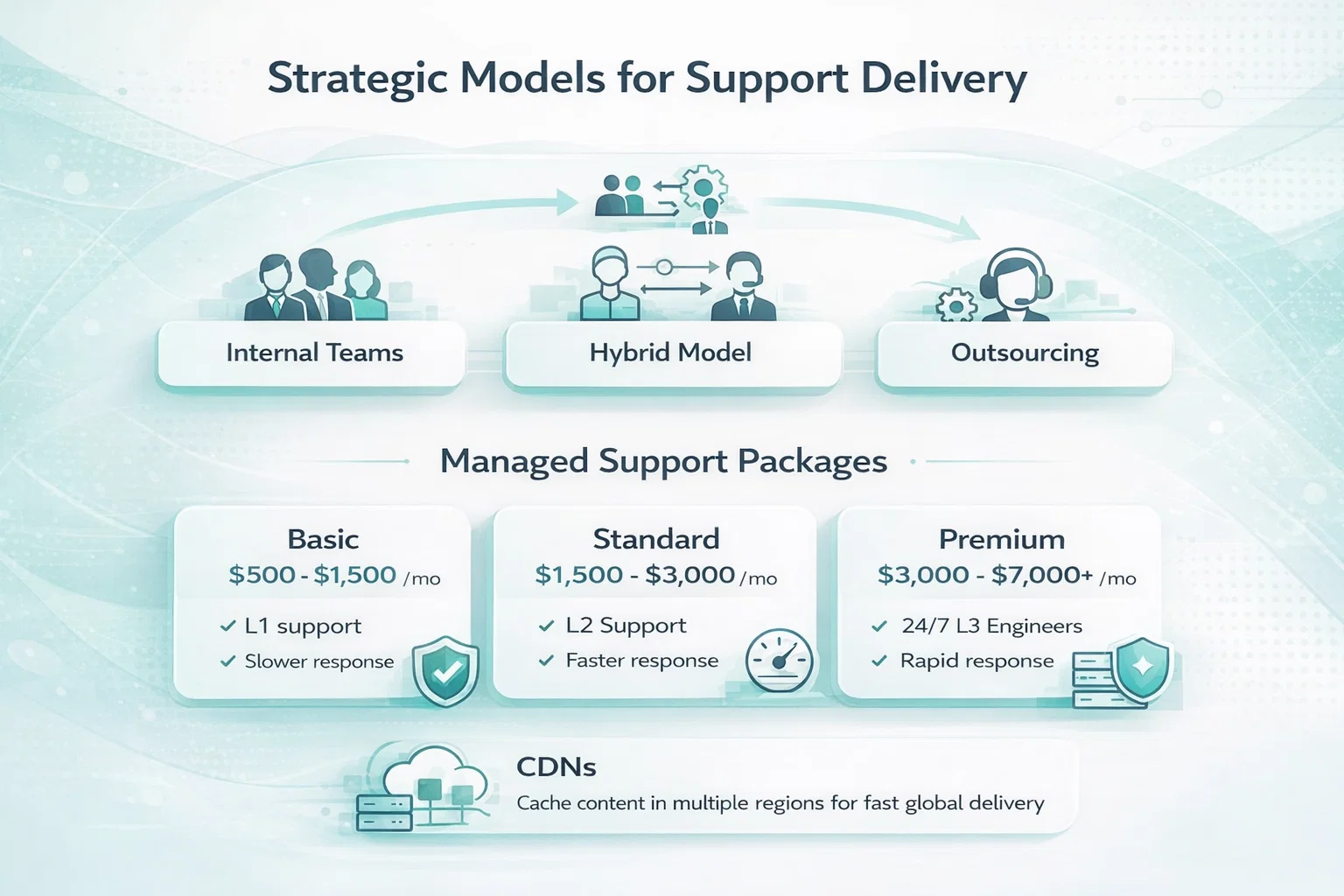
Strategic Models for Support Delivery
Support staffing requires balancing control with cost-efficiency. Organizations typically utilize internal teams, specialized outsourcing partners, or hybrid models.
Internal teams offer the deepest knowledge of the product and better alignment with the brand’s culture. However, the overhead of salaries, benefits, and training can be prohibitive for smaller companies. Outsourcing allows for rapid scaling and access to a broader range of specialized skills without the long-term commitment of full-time hires.
Managed Support Packages
Many service providers offer tiered subscription models to provide predictability in budgeting.
- Basic Packages: Often starting around $500 to $1,500 monthly, focusing on L1 support and critical security patches with slower response times (24-48 hours).
- Standard Packages: Ranging from $1,500 to $3,000 monthly, these usually include L2 support, regular performance reports, and faster response windows (8-24 hours).
- Premium Packages: Costing between $3,000 and $7,000+ monthly, these provide 24/7 coverage, dedicated L3 engineering resources, and rapid response times (1-4 hours).
Average Cost Benchmarks and Regional Variations
Calculating a support budget requires balancing technical necessity with geographic economic realities. The following breakdown illustrates how initial development costs and location influence the final expenditure.
Standard Maintenance Investment
In 2026, businesses should expect to spend 15% to 25% of their initial development cost on annual maintenance. A project costing $100,000 to build typically requires a yearly support budget of $15,000 to $25,000. Enterprise-level platforms often see these figures escalate significantly based on their scale and the criticality of their uptime.
Global Labor Rates and Geographic Impact
Geographic location remains a primary factor in labor costs, influencing the total investment required for technical teams. Regional differences often determine the volume of support an organization can afford within a fixed budget.
| Région | Estimated Hourly Rate | Service Characteristics |
| North America | $150 – $250 | High labor costs, local time-zone alignment |
| Eastern Europe | $35 – $70 | High technical quality, cost-effective scaling |
| Asia & Other Regions | Variable lower rates | Lowest entry point, potential time-zone gaps |
Estimated Costs by App Complexity
Simple applications with basic functionality usually require an annual budget between $5,000 and $15,000. These apps typically don’t have high traffic or complex backends, so maintenance is mostly focused on OS updates and occasional bug fixes.
Mid-sized applications with several hundred thousand users and multiple integrations often see annual costs between $30,000 and $70,000. Large-scale enterprise solutions or mission-critical platforms can easily exceed $150,000 per year, as they require 24/7 monitoring, dedicated support teams, and high-frequency security updates.
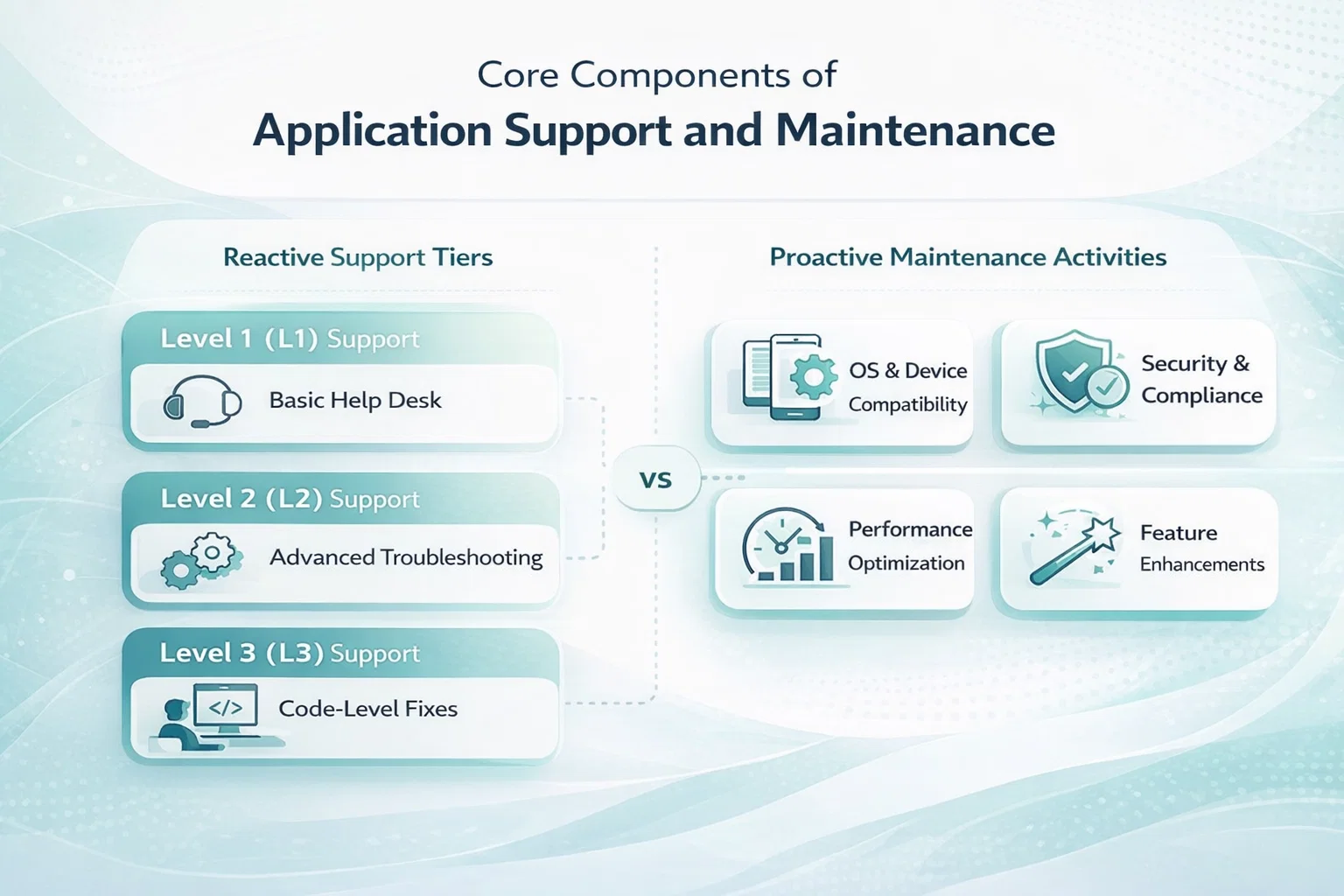
Core Components of Application Support and Maintenance
Support and maintenance are distinct technical functions. Support is user-centric, focusing on troubleshooting access, feature guidance, and managing service requests. Maintenance, on the other hand, is system-centric. It focuses on the internal health of the application, including code refactoring, server optimization, and compatibility updates.
The scope of these services is often categorized into reactive and proactive measures. Reactive support deals with issues after they occur, such as fixing a broken payment gateway or resetting a user’s password. Proactive maintenance seeks to prevent issues before they manifest by monitoring performance metrics, conducting security audits, and updating libraries to avoid technical debt. Both are essential for a healthy software lifecycle.
Reactive Support Tiers
Standard industry practice divides reactive support into three distinct levels, each requiring a different degree of technical expertise and cost allocation.
Level 1 (L1) Support
This is the front line of communication. Staff at this level handle high-volume, low-complexity requests like login assistance or basic navigation queries.
Level 2 (L2) Support
When a problem cannot be solved with standard procedures, it moves to L2. These specialists handle configuration changes and deeper troubleshooting without altering the source code.
Level 3 (L3) Support
This tier involve developers and system architects. They address complex defects that require changes to the application’s code or database structure.
Proactive Maintenance Activities
Proactive maintenance ensures compatibility with annual iOS and Android updates, preventing breaking changes in the codebase. This approach avoids service interruptions by addressing platform shifts before they impact users.
System health monitoring tracks load times and server responses to identify bottlenecks and prevent crashes. The scope of proactive support typically includes:
- OS and Device Compatibility: Adjusting code for new hardware and the latest mobile operating system versions.
- Security Patching and Compliance: Updating encryption protocols and libraries to meet standards like GDPR or HIPAA.
- Optimisation des performances: Tuning database queries and server resources to handle increasing user traffic.
- Feature Enhancements: Refining functionalities based on user feedback and current market trends.
Routine security audits identify potential failure points early, reducing the need for expensive emergency repairs. For businesses handling sensitive data, these audits are a mandatory operational expense to ensure long-term stability.
Why Partner with A-Listware for Application Support?
Au A-Listware, we don’t view support as a mere “bug-fixing” service, but as a strategic partnership designed to ensure your product’s longevity. We understand that as your business scales, your application requires more than reactive patches-it needs the technical excellence and execution power that we bring to every project.
We specialize in bridging the technical skill gaps within your organization. Whether you need to augment your existing team with specialized expertise or require us to take over the full-scale maintenance of your platform, we ensure your software remains future-ready. Our approach combines seamless integrations, proactive security audits, and continuous optimization, ensuring that your application doesn’t just run, but thrives.
By partnering with us, you leverage high-tier technical talent that focuses on long-term value. We help you eliminate technical debt and optimize infrastructure costs, ensuring that your support budget is an investment in stability and growth rather than just a cost of doing business. At A-Listware, we don’t just keep your application online; we ensure it is always ready for the next stage of your digital evolution.
Determining Factors of Support Budgets
Support budgets depend on application architecture.
Complexity is the most significant driver of ongoing expenses. An application with numerous third-party integrations-such as CRM systems, payment processors, and marketing tools-requires more frequent monitoring. Each integration point is a potential failure zone that must be checked whenever any of the connected systems undergo an update.
- App Complexity and Codebase: Larger systems with custom-coded features require more specialized engineers for L3 support.
- Infrastructure and Hosting: Monthly fees for cloud servers, databases, and Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) scale with user traffic and data storage needs.
- Compliance and Security: Industries like finance and healthcare face higher costs due to mandatory audits and strict data protection regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA.
- Technical Debt: Older legacy systems often experience more frequent failures, requiring a larger portion of the budget for “corrective” maintenance.

Optimization and Cost-Saving Strategies
Reducing the cost of support should never come at the expense of application stability. Instead, organizations should focus on efficiency and prevention. One of the most effective ways to lower long-term costs is to invest in high-quality code during the development phase. Clean, well-documented code is easier and faster to fix than “spaghetti code” that was rushed to market.
Automation also plays a growing role in cost reduction. AI-driven monitoring tools can detect anomalies in server behavior or user patterns and trigger automated fixes or alerts before a human agent is even aware of the issue. This reduces the number of man-hours spent on routine observation.
- Self-Service Resources: Developing comprehensive FAQs and help centers can deflect up to 70% of common L1 queries, drastically reducing the need for human agents.
- Tests automatisés: Implementing regression tests ensures that new updates don’t break existing features, preventing expensive emergency repairs.
- Regular Refactoring: Addressing technical debt incrementally prevents it from snowballing into a major system failure that requires a total overhaul.
- Strategic Outsourcing: Using offshore or nearshore teams for routine maintenance can cut labor costs by more than half while maintaining high technical standards.
The Long-Term Value of Sustained Support
Sustained maintenance preserves software as a functional asset. Regular updates ensure speed and security, reducing the need for full re-development and preventing revenue loss from downtime.
In the current digital economy, users have little patience for slow or broken apps. Consistent investment in support ensures that the software stays competitive and continues to meet the strategic objectives of the business. By viewing support as an investment in quality rather than just a running cost, companies can build more resilient and scalable digital solutions.
Conclusion
Application support costs in 2026 are influenced by a mixture of technical complexity, regional labor rates, and the required level of responsiveness. While the industry standard of 15-25% of initial development costs serves as a helpful baseline, every project requires a tailored approach. By categorizing tasks into tiers, prioritizing proactive maintenance over reactive fixes, and leveraging global talent pools, businesses can maintain high-performing software while keeping budgets under control. Ultimately, the goal is to find the right balance that ensures stability today and scalability tomorrow.
FAQ
- What is the difference between application support and maintenance?
Support focuses on helping users and solving immediate issues with app utilization, while maintenance involves the background technical work needed to keep the software stable, secure, and compatible with new technologies.
- How much should I budget for annual app support in 2026?
A general rule is to reserve 15% to 25% of your original development cost. For simple apps, this may be $5,000 to $15,000 annually, while complex enterprise systems can range from $50,000 to over $150,000.
- Why is L3 support more expensive than L1 or L2?
L3 support requires senior software engineers or architects who can dive into the source code and database to fix deep-rooted bugs or performance issues, whereas L1 and L2 handle more surface-level tasks.
- Does my app really need 24/7 support?
This depends on your user base and the criticality of the app. If you run a global e-commerce platform or a mission-critical business tool, 24/7 support is necessary to prevent significant revenue loss during outages.
- Can I reduce my maintenance costs by using AI?
Yes, AI-driven monitoring and automated testing tools can reduce the manual effort required for system observation and bug detection, often saving 15% to 25% on support operations over time.
- How often does an app need compatibility updates?
Ideally, you should plan for significant updates at least once or twice a year to align with major iOS and Android releases, plus monthly minor updates for security patches and small bug fixes.
- Is it better to hire an in-house support team or outsource?
Outsourcing is generally more cost-effective and provides access to diverse expertise, making it ideal for most businesses. In-house teams are better for highly specialized, proprietary systems where deep internal knowledge is a priority.


